Understanding Diabetes: Types, Symptoms, and Early Warning Signs
The IDF Diabetes Atlas (2021) report states that 10.5% of the adult population (aged between 20-79 years) around the world has diabetes, with projections showing that by 2045, 1 in 8 adults will be diabetic. The most common reasons quoted for this are the changing dynamics in population and lifestyle habits, with an increase in the aging population, urbanization, decreased levels of physical activity, and the prevalence of obesity.
What is Diabetes?
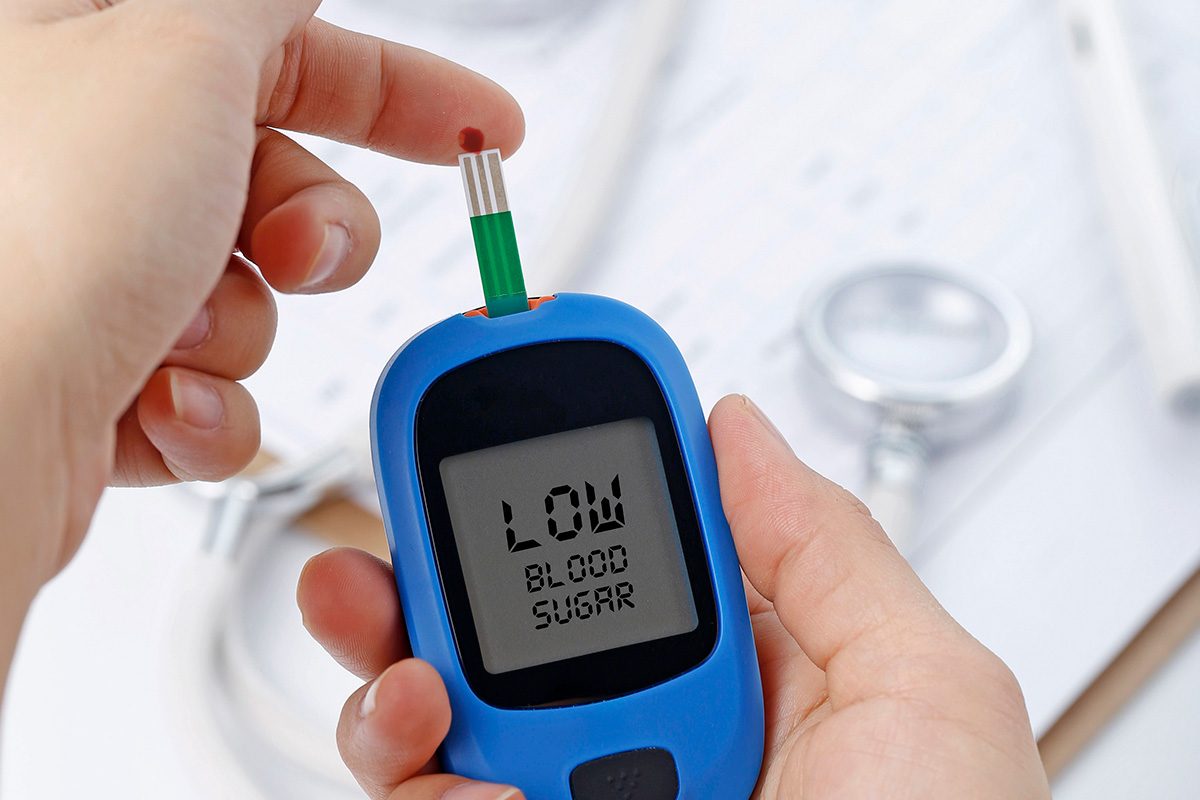
When a person’s pancreas does not make sufficient amounts of insulin, or the body does not actively respond to the effects of the insulin, it causes the person’s blood glucose levels to rise rapidly. This condition is known as diabetes. It can occur in people of any age and almost all types of diabetes are chronic but can be managed with the support of medication and lifestyle modifications.
Types of Diabetes
There are various types of diabetes but the four most common types are:
Type1 Diabetes
An autoimmune disease usually diagnosed in children and young adults, Type 1 diabetes is caused when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the pancreatic cells that produce insulin. Insulin is the hormone that enables blood glucose to enter the body cells and be used as energy. Lack of sufficient levels of insulin causes the blood glucose to build up in the bloodstream instead of entering the cells, which spikes the level of blood glucose and causes complications in the body.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is also known as insulin resistance when the body does not use the produced insulin in the right way. The body cells try to compensate for this by producing more insulin in the short term, but over time, the pancreas becomes unable to produce sufficient insulin to keep the blood glucose levels normal. Type 2 diabetes is less common in children, it is usually seen in adults.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is the stage before diabetes when the blood glucose levels in the body are higher than normal levels but it has not reached the lower limit set for Type 2 diabetes diagnosis. With lifestyle adjustments and a healthy diet, it may be possible to bring the blood glucose levels back within the normal range at this stage.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes (GDM) is diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. While the exact cause of gestational diabetes is unclear, studies have shown that the hormones in the placenta that support a fetus growth sometimes block the mother’s insulin, which leads to insulin resistance during the period of pregnancy. The key to managing gestational diabetes and protecting both the mother and the baby is through early diagnosis and treatment.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore
People who have diabetes show some visible symptoms which can be an early indication of the onset of diabetes.
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes can develop rapidly over a period of a few weeks or months. The endocrinologist may ask a person to check for Type 1 diabetes if one or more of the below symptoms are present:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia) and dry mouth
- Excessive hunger, even after a meal
- Extreme fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurring of vision
- Cuts or bruises take longer to heal
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes may not be noticed because they develop slowly, over a long period of time. In addition to the symptoms seen in Type 1 diabetic patients, people with Type 2 diabetes may also notice
- Tingling sensation, pain, or numbness in their hands or feet
- Frequent skin infections and/or vaginal yeast infections
Complications of Untreated Diabetes
Diabetes is not a standalone health issue. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a host of other health issues affecting the heart, kidney, vision, neuropathy, skin issues, dental health problems like gingivitis and periodontitis, hearing loss, complications with the foot including nerve damage, reduced blood circulation or even loss of limbs, increased stroke risk, and even life-threatening complications like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) which is caused by an overload of a body chemical called ketones that makes the blood acidic.
How Can Taha Medical Centre Help with Diabetes Diagnosis and Management?
Taha Medical Centre is a leading medical clinic in Abu Dhabi for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes. With highly qualified expert diabetologists, highly trained and experienced medical and nonmedical teams, advanced laboratory and diagnostic equipment, and stringent hygiene standards and infection control measures, we are best suited to address the needs of patients with diabetes, whether it is for diabetic screenings or treatment of various types of diabetes. In addition to the treatment and monitoring of diabetic patients in the clinic, we also have a specialized team to offer diabetes counseling to explain the dietary requirements and lifestyle modifications to be made. Our medical clinic in Abu Dhabi is also equipped to handle other health issues or complications that may result from diabetes.